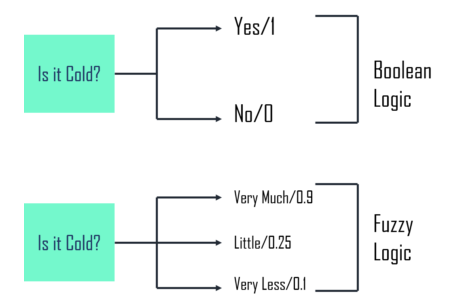
In the real world we come across situations where we can’t determine that the state is true or false. Here comes fuzzy logic which provides flexibility for reasoning. This method of reasoning resembles human reasoning. It provides all intermediate possibilities between YES or NO.
Fuzzy Logic Systems Architecture
It contains four main parts
Rules:
It consists of set of rules and IF-THEN conditions provided by the experts.
Fuzzifier:
It transforms the system inputs, which are crisp numbers into fuzzy sets. Crisp inputs are mostly the exact inputs measured by sensors and passed into the control system for processing, such as temperature, pressure etc. It divides the input signal into five steps such as
| LP | x is Large Positive |
| MP | x is Medium Positive |
| S | x is Small |
| MN | x is Medium Negative |
| LN | x is Large Negative |
Interface Engine:
It determines the matching degree of the current fuzzy input with respect to each rule and decides which rules are to be fired according to the input field. Next, it combines the fired rules to form the control actions.
Defuzzifier:
It transforms the fuzzy sets obtained by the interface engine into a crisp value.
Membership function
The membership function is a graph that defines how each point in the input space is mapped to membership value between 0 and 1. A membership function on the universe of discourse X for a fuzzy set A is defined as μA:X → [0,1].
The degree of membership of the element in X to the fuzzy set A is quantified.
- x-axis signifies the universe of discourse.
- y-axis signifies the degrees of membership in the [0, 1] interval.
Simple membership functions are used as the complex functions do not add precision in the output. The membership functions for LP, MP, S, MN, and LN are:
The most common among various other membership function shapes is the triangular membership function shapes. Here, the input to 5-level fuzzifier varies from -10 volts to +10 volts. Hence the corresponding output also changes.
Application Areas of Fuzzy Logic
Automotive Systems
- Automatic Gearboxes
- Four-Wheel Steering
- Vehicle environment control
Consumer Electronic Goods
- Hi-Fi Systems
- Photocopiers
- Still and Video Cameras
- Television
Domestic Goods
- Microwave Ovens
- Refrigerators
- Toasters
- Vacuum Cleaners
- Washing Machines
Environment Control
- Air Conditioners/Dryers/Heaters
- Humidifiers
Advantages of Fuzzy Logic Systems
- The structure is easy and understandable.
- Flexibility allows you to modify a FLS by just adding or deleting rules.
- Mostly robust as no precise inputs required.
- Little memory is required as the algorithms are described with little data.
Disadvantages of Fuzzy Logic Systems
- For designing fuzzy system there is no systematic approach.
- It is a difficult task in Setting exact, fuzzy rules and, membership functions.
- The probability theory confuses the fuzzy logic.