Docker Installation in Ubuntu
We’re going to install Docker from the official Docker repository to make sure we get the latest version. The official Docker repository may not have the latest version. We’re gonna add a new package source, add Docker’s GPG key, and then install the package.
- Update your package list first:
$ sudo apt update- Next, install a few prerequisites so that apt can use HTTPS packages:
$ sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common- The official Docker repository’s GPG key is here:
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -- The Docker repository should be added to APT:
$ sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal stable"Docker packages from the newly added repo will also be added to our package database.
- Make sure you’re installing from the Docker repo instead of the Ubuntu repo:
$ apt-cache policy docker-ceThe output will look like this, although Docker may have a different version number:
Output:
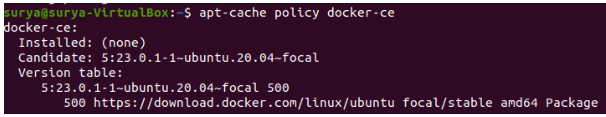
You’ll notice that docker-ce isn’t installed, but you can install it from the Docker repository for Ubuntu 20.04 (focal).
- Install Docker:
$ sudo apt install docker-ceCheck that Docker is installed, the daemon is running, and the process is enabled to start on boot:
- To check the status of the Docker:
$ sudo systemctl status dockerIf the service is active and running, the output should look like this:
Output:
Docker now comes with not just the Docker service (daemon), but also the Docker client. We’ll look at how to use the docker command later.
Docker Commands Without Sudo (Optional)
It’s only possible to run the docker command by the root user or by the docker group, which is created automatically when Docker is installed. When you run the docker command without sudo or without being part of the docker group, you’ll get this:
docker: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon. Is the docker daemon running on this host?. See 'docker run --help'.
Add your username to the docker group to avoid typing sudo:
$ sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}Log out and back in again to apply the new group membership, or type:
$ su - ${USER}To continue, you’ll need to enter your password.
Type: to confirm your user has been added to the docker group:
$ groupsOutput:
surya sudo dockerDeclare a username explicitly if you need to add someone to the docker group who isn’t logged in:
$ sudo usermod -aG docker usernameRun the docker command as sudo if you don’t want to run it as a member of the docker group.