Git Undo’s
In Git, “undo” can refer to several different operations that allow you to revert changes or return to a previous state in your repository. Here are a few common ways to undo changes in Git:
- Undo will be done only for the existing files.
git checkout: You can use git checkout to switch to a different branch or to discard changes in your current branch.
For example, git checkout HEAD will discard all uncommitted changes in your working directory.
Undo in the working area:
If a file is created and not added to indexing area and if it has been checkout to another branch, the file will not be saved or the file has be undo in the working area.

In the above shown image, as we can see that there is a file ‘newfile’. We have modified the file by added the content ‘This is a newfile’ , as we can see that the file was under untracked files in the git status , but when we used the command below the content in the file has been undone or not saved.
git checkout <file-name>git reset: git reset allows you to undo commits and move the branch pointer to a previous state. The –hard option discards all changes in the branch, while the –soft option only undoes the commits, preserving the changes in the working directory.
Undo in the Indexing area :
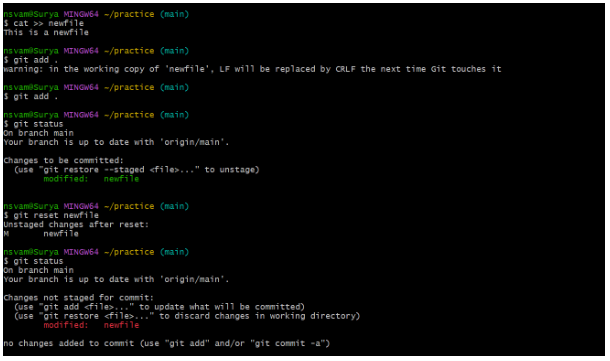
As we can see that the file has been modified and added to the indexing area(we can see in the git status). In order to undo in the indexing area we used the below command and the files has came back from the indexing area to the working area.
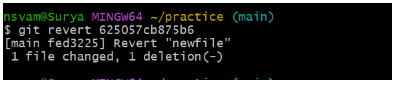
git reset <file-name>git revert: git revert is used to undo committed changes by creating a new commit that undoes the changes introduced in a previous commit. Unlike git reset, git revert does not discard commits, but instead creates a new commit that “reverses” the changes of a previous commit.
git stash: git stash allows you to temporarily save changes that you don’t want to commit yet, and then reapply them later. This can be useful if you need to switch to a different branch but don’t want to commit your changes.
It’s important to be cautious when using Git’s undo features, as they can permanently discard changes or make it difficult to recover from mistakes. Be sure to make a backup of your repository before making any destructive changes.
To temporarily save
$ git stash save
To see the stash ID.
$ git stash list
To unstash the file.
$ git stash apply stash-ID / git stash pop stash-ID After unstashing a file, commit and push to the remote repository.
