JavaScript ternary operator
When coding in any language, we use various methods to handle conditional situations. In JavaScript, we can use the ternary operator instead of the if statement. A ternary operator assigns a value to a variable based on a condition.
This is the only JavaScript operator that takes three operands. It works in the same manner as an if-else conditional statement. In other words, it is a shortcut for the if-else statement.
This operator consists of three operands: a condition followed by a question mark (?) and two expressions separated by a colon (:). When the condition is true, the first expression is executed, and when it is false, the second expression is executed.
Syntax
var a = (condition) ? expr1 : expr2; In the above syntax, condition, expr1, and expr2 are the three operands of the ternary operator. A value is assigned to the variable ‘a’ based on the condition provided. After evaluating the condition as a Boolean value, the operator assigns the result to the variable. A first expression is assigned to the true value of the condition and a second expression is assigned to the false value of the condition.
Example
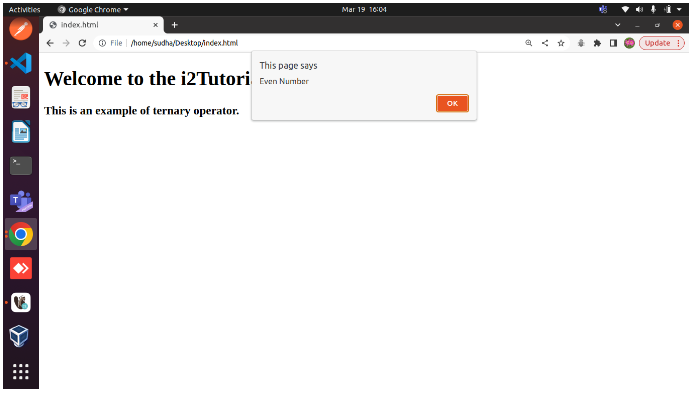
This is a simple example of using the ternary operator to determine whether the number is odd or even. Using the alert() dialog box, the result will be displayed.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script> let a = 358; let val = ( a % 2 == 0) ? 'Even Number' : 'Odd Number'; alert(val); </script> </head> <body> <h1> Welcome to the i2Tutorials </h1> <h3> This is an example of ternary operator. </h3> </body> </html>