MySQL – INSERT Record

An INSERT statement is used in MySQL to add records to a table. As a basic rule, the syntax of the INSERT statement is as follows:
syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
Example:
Below is an example of how to use the INSERT statement to add a new record to a table called “employees”:
INSERT INTO employees (emp_no, Name, Email) VALUES (5, 'John', 'John@gmail.com');
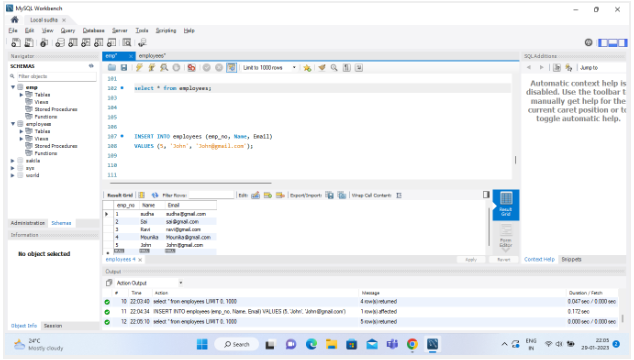
An employee record would be created in the “employees” table with the values 5 for “emp_no”, ‘John’ for “Name,” and ‘John@gmail.com” for “Email.”.
The INSERT statement can also be used to insert multiple records at once by providing multiple sets of values:
INSERT INTO employees (emp_no, Name, Email) VALUES (6, 'lucky', 'lucky@gmail.com'), (7, 'Swathi', 'Swathi@gmail.com');
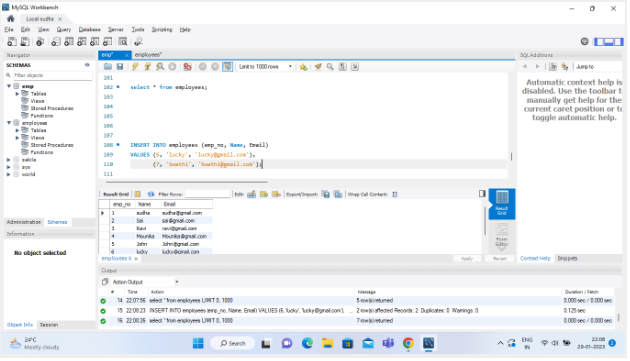
This would insert 2 new records into the “employees” table with the values 6 and 7 for “employee_id”, ‘lucky’ and ‘swathi’ for “Name”, ‘lucky@gmail.com’ and ‘Swathi@gmail.co’ for “Email” .
Note:
It is important that the order of the columns in the INSERT statement matches the order of the columns in the table definition.
