MySQL – LIKE

The LIKE condition in MySQL is used to match patterns to obtain the correct results. With the use of WHERE clauses, it is used in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements.
Syntax:
expression LIKE pattern [ ESCAPE 'escape_character' ] expression – This specifies the name of a column or field.
Pattern – There is a pattern matching component in this character expression.
escape_character – The option is optional. There is an option to test for literal instances of a wildcard character, such as % or . If you do not specify the escape character, MySQL will assume “/” is the escape character.
Examples:
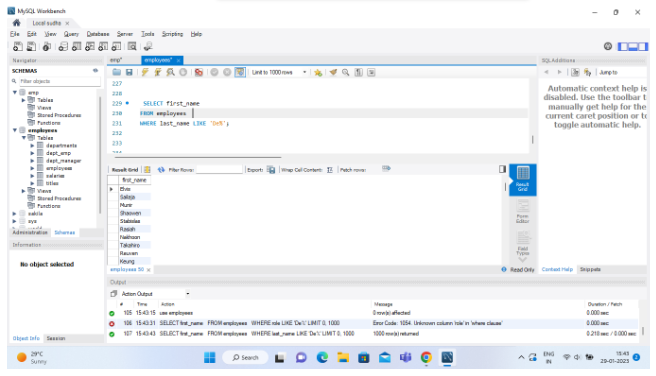
1.Using % :
SELECT first_name FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE 'De%';
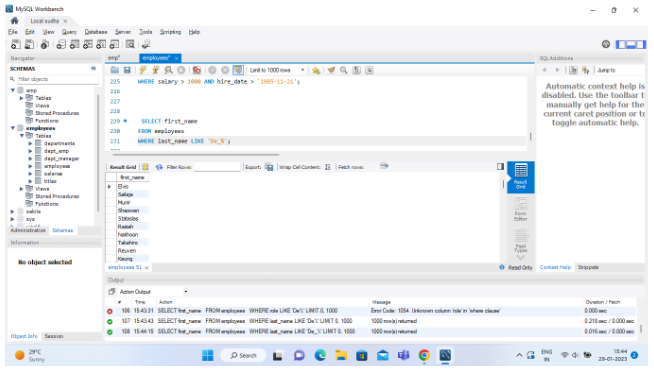
2.Using _ :
SELECT first_name FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE 'De_%';
As an example of different LIKE operators with ‘%’ and ‘_’ wildcards, the following examples are provided:
| LIKE Operator | Description |
| LIKE ‘a%’ | Searches for values that begin with “a” |
| LIKE ‘%a’ | Searches for values that end in “a” |
| LIKE ‘%or%’ | This function finds any values containing “or” at any position in the value |
| LIKE ‘_r%’ | Searches for values that have “r” in the second position |
| LIKE ‘a_%’ | Searches for values that begin with “a” and have at least two characters |
| LIKE ‘a__%’ | This function finds any value that begins with “a” and is at least three characters in length |
| LIKE ‘a%o’ | Searches for values that begin with “a” and end with “o” |
