Python | Enum
Enumerations are executed by using the module named “enum“in Python.By using classes enumerations are created . Enums have names and values related with them.
Features of enum:
- Enums are shown as string or repr.
- Enums use type()to check their types.
- Enums uses “name” keyword display the name of the enum member.
Example:
import enum
# creating enumerations using class
class Animal(enum.Enum):
ant = 1
bee = 2
cat = 3
# printing enum member as string
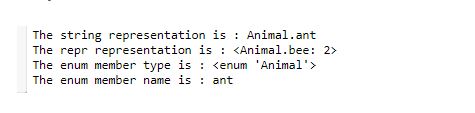
print ("The string representation is : ",end="")
print (Animal.ant)
# printing enum member as repr
print ("The repr representation is : ",end="")
print (repr(Animal.bee))
# printing the type of enum member
print ("The member type is : ",end ="")
print (type(Animal.cat))
# printing name of enum member
print ("The member name is : ",end ="")
print (Animal.ant.name)
Output:
- Enumerations are iterable. They can be iterated using loops
- Enumerations support hashing. Enums can be used in dictionaries or sets.
Example:
import enum
# creating enumerations using class
class Animal(enum.Enum):
cat = 1
bee = 2
lion = 3
# printing all enum members using loop
print ("All the enum values are : ")
for Anim in (Animal):
print(Anim)
# Hashing enum member as dictionary
di = {}
di[Animal.cat] = 'meows'
di[Animal.lion] = 'roar'
# checking if enum values are hashed successfully
if di=={Animal.cat : 'meows',Animal.lion : 'roar'}:
print ("Enum is hashed")
else: print ("Enum is not hashed")
Output:

Share:



