Tableau – Bump Chat
What is a Bump Chart?
The Bump Chart is used to compare two dimensions using one of the Measure values. They are useful for exploring changes in rank of a value over time, place, or other relevant dimensions. Therefore, bump charts can be used to compare two dimension values. In Tableau, bump charts are usually created using two dimension fields and at least one measure field.
How to create a Bump chart in Tableau?
Make your first bump chart in Tableau by following the steps below.
Step 1: Add dimension and measures
To begin creating a bump chart, open a new worksheet in Tableau Desktop or whatever version you are using. First, we need to add two dimensions and a measure. Using our dataset (sales of an electronics store), we add Order Date and Region from the Dimensions section and Sales from the Measures section.
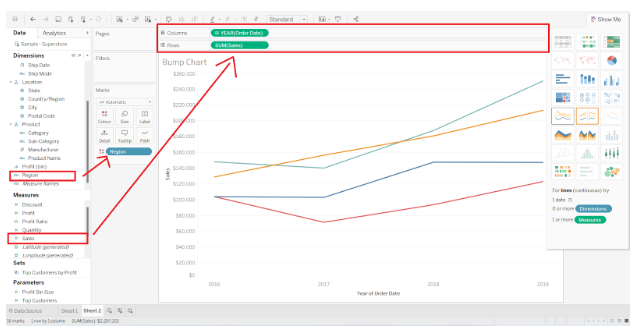
Note : In the Marks pane, we have added YEAR(OrderDate) to the Columns section, SUM(Sales) to the Rows section, and Region to the Color box of Marks pane.
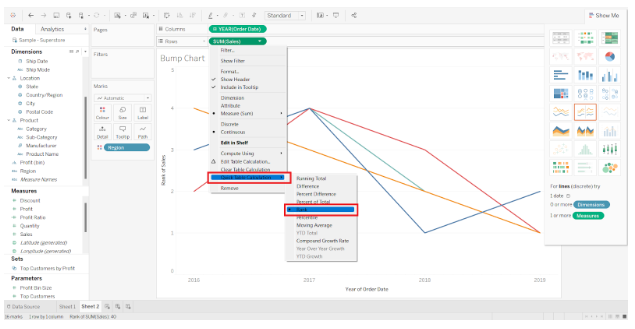
Step 2: You may select a Quick Table Calculation
You can access options for the SUM(Sales) field by right-clicking on it. We select Quick Table Calculation from the drop-down list, followed by Rank.
Step 3: A field to computed should be selected
Next, we right-click on the SUM(Sales) field to access its options. Our computing criteria is Region, which we select that from the drop-down list under Compute Using.
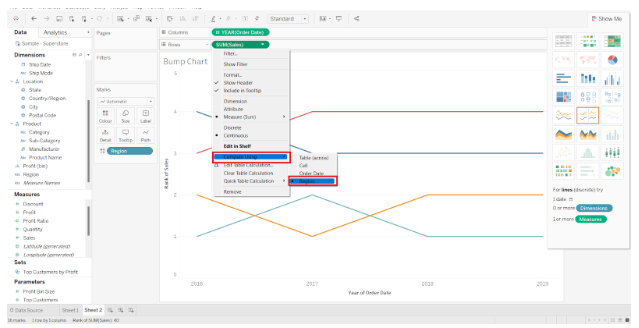
By doing this, the lines of the line chart will be arranged according to the rank of their data points. Currently, those measure values are continuous, which needs to be changed to discrete.
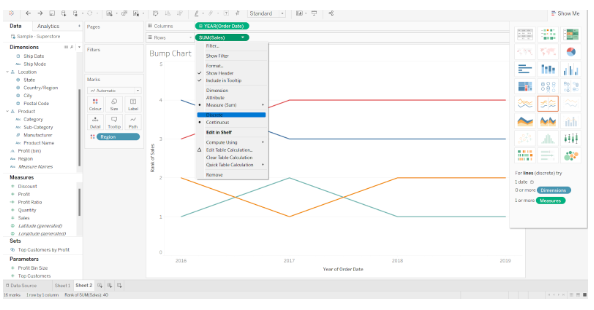
By default, the chart is in Standard view mode. If we want to fit the chart on the editing canvas, we can change the mode to Entire View.
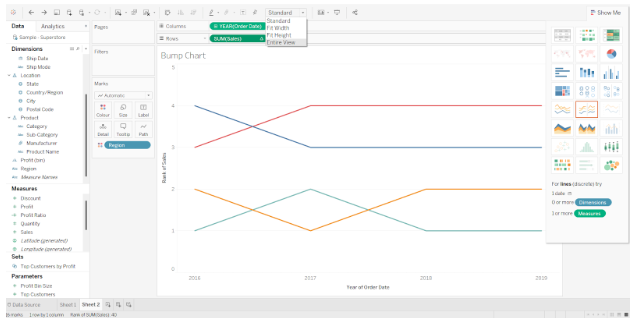
Step 4: Duplicate measure
The next step is to duplicate our measure SUM(Sales). As shown in the screenshot below, this will result in two separate line charts.

Step 5: Modify mark type
Creating a bump chart requires converting the mark type of the second (duplicate) line chart measure SUM(Sales). The mark type of this measure is changed from lines to circles. From the drop-down list of mark types, select Circle.

To display rank labels on the circles of the second chart, click on the Show mark labels option in the Labels box. Labels can be formatted with more options in the label editor.
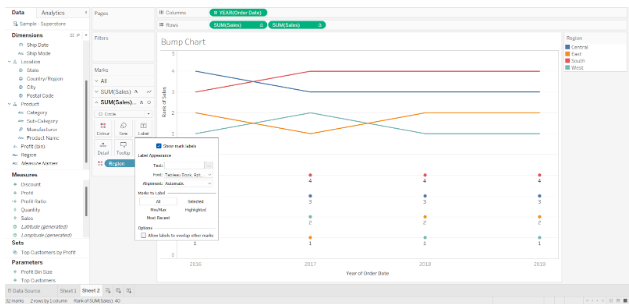
Currently, we have two different charts, one showing the data trends with a line, and the other showing data points with circles and ranks. In order to make a bump chart, we need to merge these two charts together. Right-click on the measure field SUM(Sales) and select Dual Axis from the drop-down menu.
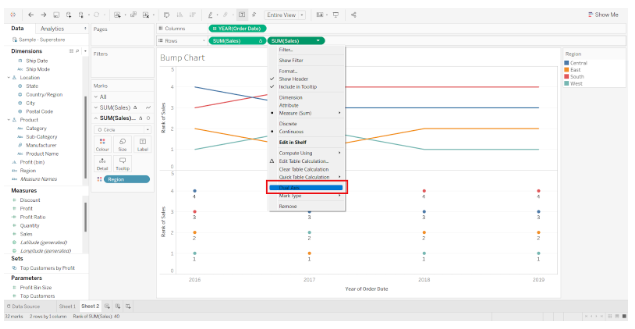
As a result, the two charts are merged into one chart, and one additional axis is added to the right.
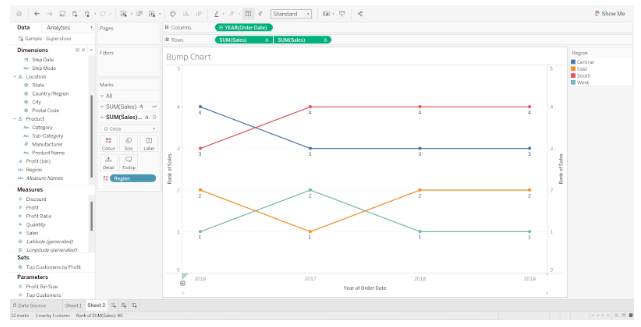
Step 7: Final Bump chart
Our bump chart is now complete. We made this bump chart in tableau to show year-by-year sales for four regions and their progression over time. The four regions of Central, East, South, and North are assigned specific colors.
For the Central region, which is indicated in yellow, the total sales remained 3rd for two consecutive years, 2016 and 2017. In 2018, it fell to 4th place, but regained third place in 2019.

As a result, bump charts represent rank-wise progression of data points with respect to a given dimension.
Conclusion
You can easily create bump charts in Tableau using this method. If you want to analyze two dimension values in a chart based on rank, you can choose a bump chart.
