Tableau Data Sources
To master any Business Intelligence tool, the most basic operation is to connect to a data source. Having established a connection with a data source, we can access all the data, bring some of it into Tableau’s repository (extract) and analyze it.
Tableau can connect to all popular data sources. The following types of data can be connected to Tableau’s native connectors.
- File Systems such as CSV, Excel, etc.
- Relational Systems such as Oracle, Sql Server, DB2, Tableau Server etc.
- Cloud Systems such as Windows Azure, Google BigQuery, etc.
- Other Sources using ODBC
File-Based vs Server-Based
There are two primary types of data connections in Tableau i.e —file-based and server-based.
File-Based
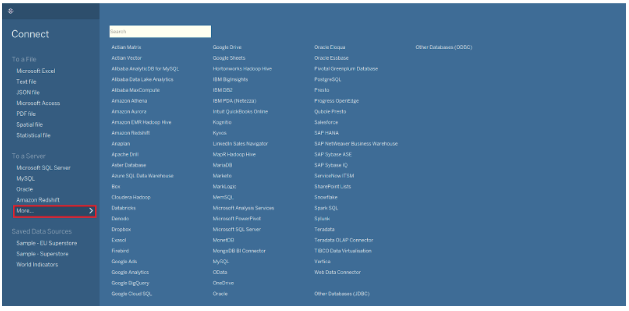
A file-based connection involves some type of file. These are listed under “To a File” in the Connect pane on the main Tableau screen.

Tableau lists Excel, text, JSON, Access, PDF, Spatial file, and Statistical file among its supported file types. However, you can connect to other Tableau workbooks and Tableau data sources by selecting the More option.
Server-Based
A server-based connection connects to a server instead of a file. Servers run some kind of software that allows you to retrieve data from them. In terms of database management systems (DBMSs), the most common examples are SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and many others.
Note: Spreadsheets and Access may seem like databases, but they are not complete “database management systems” like those listed above.
Connecting to a File
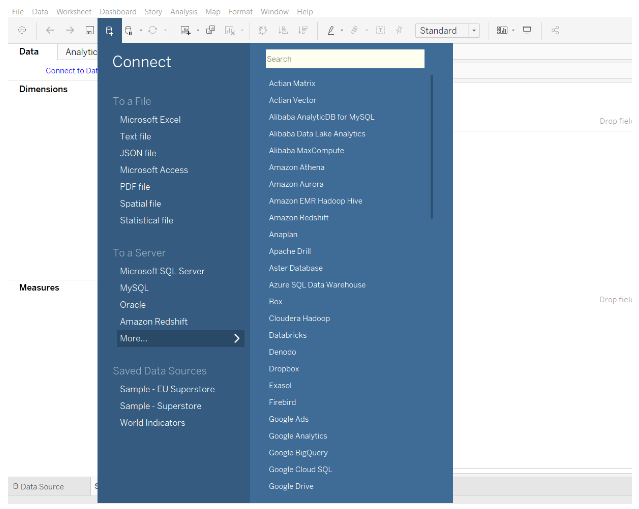
Tableau provides a variety of options for connecting to and retrieving data from files. There are several options available when connecting to a file section, including MS Excel, MS Access, JSON, text files, PDF files, spatial files, etc. Additionally, you can access your system’s data files and connect them with Tableau using the More option.
You will be prompted to open a new dialog box from which you can access your system’s files. Here is a sample Excel file that we are going to select and open.
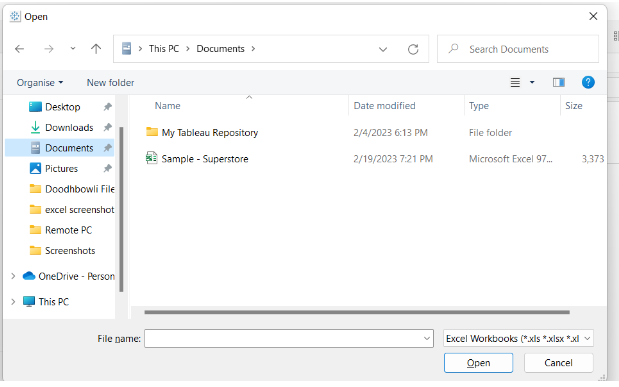
Tableau will open the Excel file in the Data Source tab.
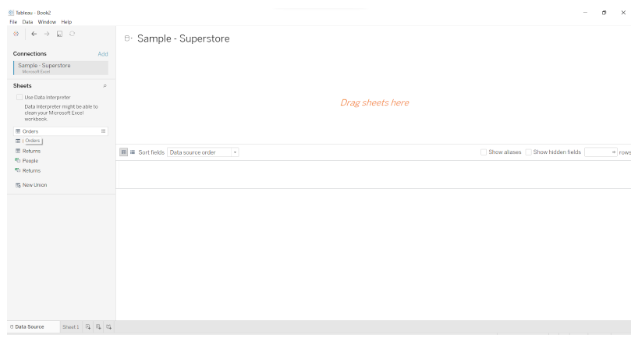
The Connections pane at the left of this tab shows the name of the data source and its contents, such as the number of sheets in an Excel file.
Data sources can be managed and viewed by dragging and dropping sheets to the central pane. You will see the entire table with the appropriate rows and columns for each sheet.
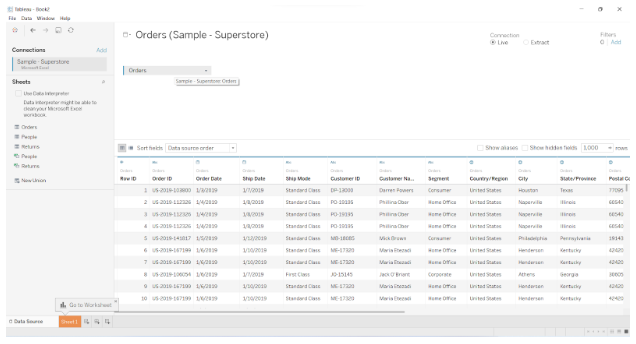
You can also add a new data source here by clicking on the Add option and selecting your desired data file or connector.
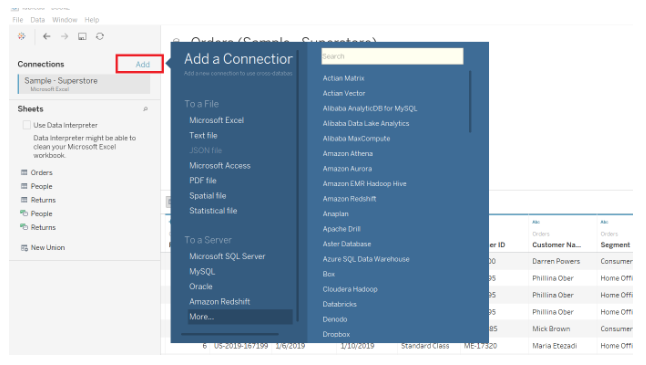
Alternatively, you can select the New Data Source option by clicking on the Data tab at the top-left of the screen.
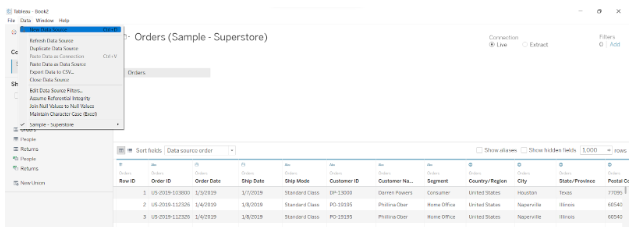
From here, we can sort fields and manage metadata, where you can see the names of all columns in their respective tables. We can also manage multiple linked data sources this way.
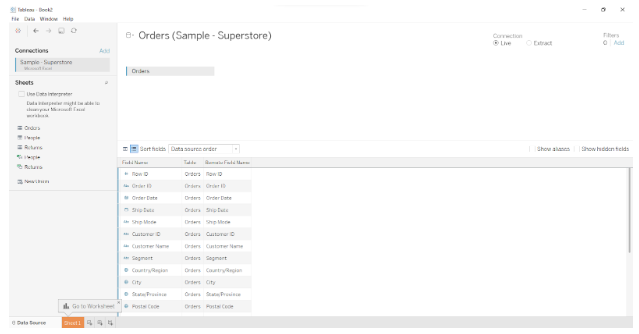
Once we have loaded our data source, we can create a Tableau worksheet. In the Sheet1 tab, just next to the Data Source tab, you will find a list of available data sources and fields. There is an organized list of dimensions and measures on the left, from which you can select and use them to create charts and graphs. Make visualizations by dragging and dropping dimensions and measures into the Columns and Rows section.

In order to establish a connection with a data source, especially one that is server-based, there are different steps to follow. In Tableau, follow the steps, provide the necessary information, and begin analyzing your data.
