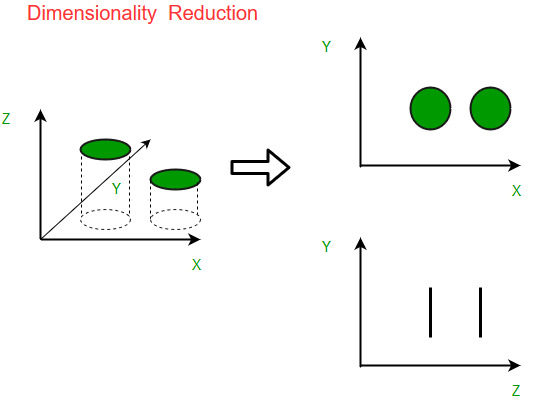
Dimensionality reduction is the process of reducing the number of random variables under consideration, by obtaining a set of principal variables. It can be divided into feature selection and feature extraction. The higher the number of features, the harder it gets to visualize the training set and then work on it. Sometimes, most of these features are correlated, and hence redundant. This is where dimensionality reduction algorithms come into play.
There are two components of dimensionality reduction:
Feature selection:
In this, we try to find a subset of the original set of variables, or features, to get a smaller subset which can be used to model the problem. It usually involves three ways:
- Filter
- Wrapper
- Embedded
Feature extraction:
This reduces the data in a high dimensional space to a lower dimension space, i.e. a space with lesser no. of dimensions.
The various methods used for dimensionality reduction include:
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
- Generalized Discriminant Analysis (GDA)
Advantages of Dimensionality Reduction
- It helps in data compression, and hence reduced storage space.
- It reduces computation time.
- It also helps remove redundant features, if any.
Disadvantages of Dimensionality Reduction
- It may lead to some amount of data loss.
- PCA tends to find linear correlations between variables, which is sometimes undesirable.
- PCA fails in cases where mean and covariance are not enough to define datasets.
- We may not know how many principal components to keep- in practice, some thumb rules are applied.