The mechanism of diffing one tree with another to determine which parts are required to be changed and then update the original DOM with it is called Reconciliation in react.
The reconciliation process helps React work faster. Through the reconciliation process the react browser Dom is updated.
The important concepts behind the working of reconciliation process are:
- Virtual Dom
- Diffing Algorithm
ReactJS is declarative. It means ReactJS abstracts away many low level operations like DOM manipulation from the developers. With that, ReactJS also makes sure to take more extra care to tackle the possible performance issues due to frequent DOM(Document Object Model) manipulation and rendering.
The term rendering in React can can be identified as making or becoming.
In traditional rendering, The browser creates a DOM (Document Object Model) represented by a tree structure and renders any new data to the DOM even if data is similar to previous ones.
This rendering by Browser has a sequence of steps and is rather costly in react nature. The concept of Virtual DOM(Document Object Model) used by React makes rendering much faster.
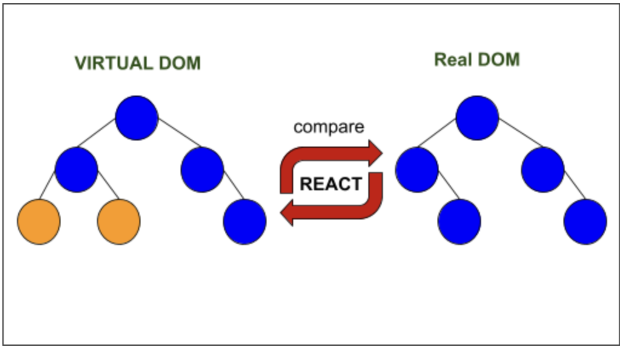
Virtual DOM: React renders JSX components to the Browser DOM(Document Object Model), while keeping a copy of the actual DOM to itself. This copy is the Virtual DOM(Document Object Model). We can think of it as the twin brother of the real or Browser DOM(Document Object Model). The following actions take place in React:
- React stores a copy of Browser DOM(Document Object Model) which is called Virtual DOM.
- When we make changes or add data, React creates a new Virtual DOM(Document Object Model) and compares it with the previous one.
- Comparison is done by Diffing Algorithm. The cool fact is all these comparisons take place in the react memory and nothing is yet changed in the web Browser.
- After comparing, React goes ahead and creates a new Virtual DOM(Document Object Model) having the changes. It is to note that as many as 200,000 virtual DOM(Document Object Model) nodes can be produced in a second.
- Then it updates the Browser DOM(Document Object Model) with the least number of changes possible without rendering the entire DOM(Document Object Model) again
Suppose we have new data similar to the previous one, Virtual DOM compares previous and new structures and sees that it has no change, so nothing gets rendered to the Browser. This is how the Virtual DOM(Document Object Model) is helping to enhance the Browser performance.
How does this Virtual DOM(Document Object Model) compare itself to its previous version?
This is where the Diffing Algorithm comes into play. Some concepts used by this Algorithm are:
- Two elements of different types will produce multiple trees.
- Breadth-First Search (BFS) is applied because if a node is found as changed, it will re-render the entire subtree hence Depth First Approach is not exactly optimal.
- When comparing two elements of the same type, keep the underlying node as the same and only update changes in attributes or styles.
- React uses optimizations so that a minimal difference can be calculated in O(N) efficiently using this Algorithm.