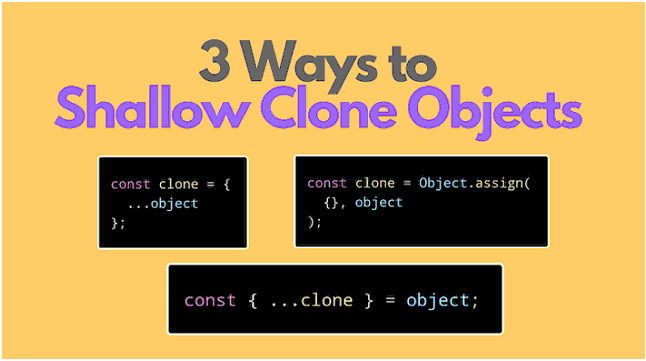
Cloning in javascript is copying an object properties to another object so as to avoid creation of an object that already exists.
There are a there ways to clone a javascript object.
1) Iterating through each and every property and copy them to a new object.
2) Using JSON method.
3) Using object.assign() method.
Iterating through each and every property and copy them to a new object:
This is an old method to clone a javascript object in which each and every property will be iterated and copied to a new object.It’s a simple method but seldom it is used.
Example:
<html>
<body>
<script>
function mSort (array) {
if (array.length === 1) {
return array // return once we hit an array with a single item
}
const middle = Math.floor(array.length / 2) // get the middle item of the array rounded down
const left = array.slice(0, middle) // items on the left side
const right = array.slice(middle) // items on the right side
return merge(
mSort(left),
mSort(right)
)
}
// compare the arrays item by item and return the concatenated result
function merge (left, right) {
let result = []
let leftIndex = 0
let rightIndex = 0
while (leftIndex < left.length && rightIndex < right.length) {
if (left[leftIndex] < right[rightIndex]) {
result.push(left[leftIndex])
leftIndex++
} else {
result.push(right[rightIndex])
rightIndex++
}
}
return result.concat(left.slice(leftIndex)).concat(right.slice(rightIndex))
}
const list = [4,7,5,9,1,3,8,2,10]
document.write(mSort(list));
</script>
</body>
</html>OUTPUT
1,2,3,4,5,7,8,9,10
JSON method:
In this method, source object must be JSON format safe.
EXAMPLE:
<html>
<body>
<p id="clone-2"></p>
<script>
const sourceObject = {name:"salman", age:23, salary:25000};
let requiredObj = {};
requiredObj = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(sourceObject));
document.getElementById("clone-2").innerHTML =
"targetObject name = "+requiredObj.name+", age = " + requiredObj.age+", salary = "+requiredObj.salary;
</script>
</body>
</html>OUTPUT:
targetObject name = salman, age = 23, salary = 25000
Object.assign():
Advanced method used very frequently using now a days to clone javascript objects.This method nothing but shallow copy which means that nested properties are still copied by reference.
EXAMPLE:
<html>
<body>
<p id="clone-3"></p>
<script>
const sourceObject = {name:"marieya", age:23, salary:25000};
let requiredObj = {};
requiredObj = Object.assign({}, sourceObject);
document.getElementById("clone-3").innerHTML =
"targetObject name = "+requiredObj.name+", age = " + requiredObj.age+",salary"+requiredObj.salary;
</script>
</body>
</html>OUTPUT:
targetObject name = marieya, age = 23,salary25000